Catalysts for PEM electrolysis
40% Platinum 20% Ruthenium on carbon black catalyst
CAS No. 7440-06-4 7440-18-8
Category: Catalysts for PEM electrolysis
parameters | value |
|---|---|
Support type | Superconductive carbon black VXC72 or VXC72R |
Color | Black powder |
Metal content | 40% Pt 20% Ru |
Metal surface | 80-120m2/g |
Particle size | 2-5nm |
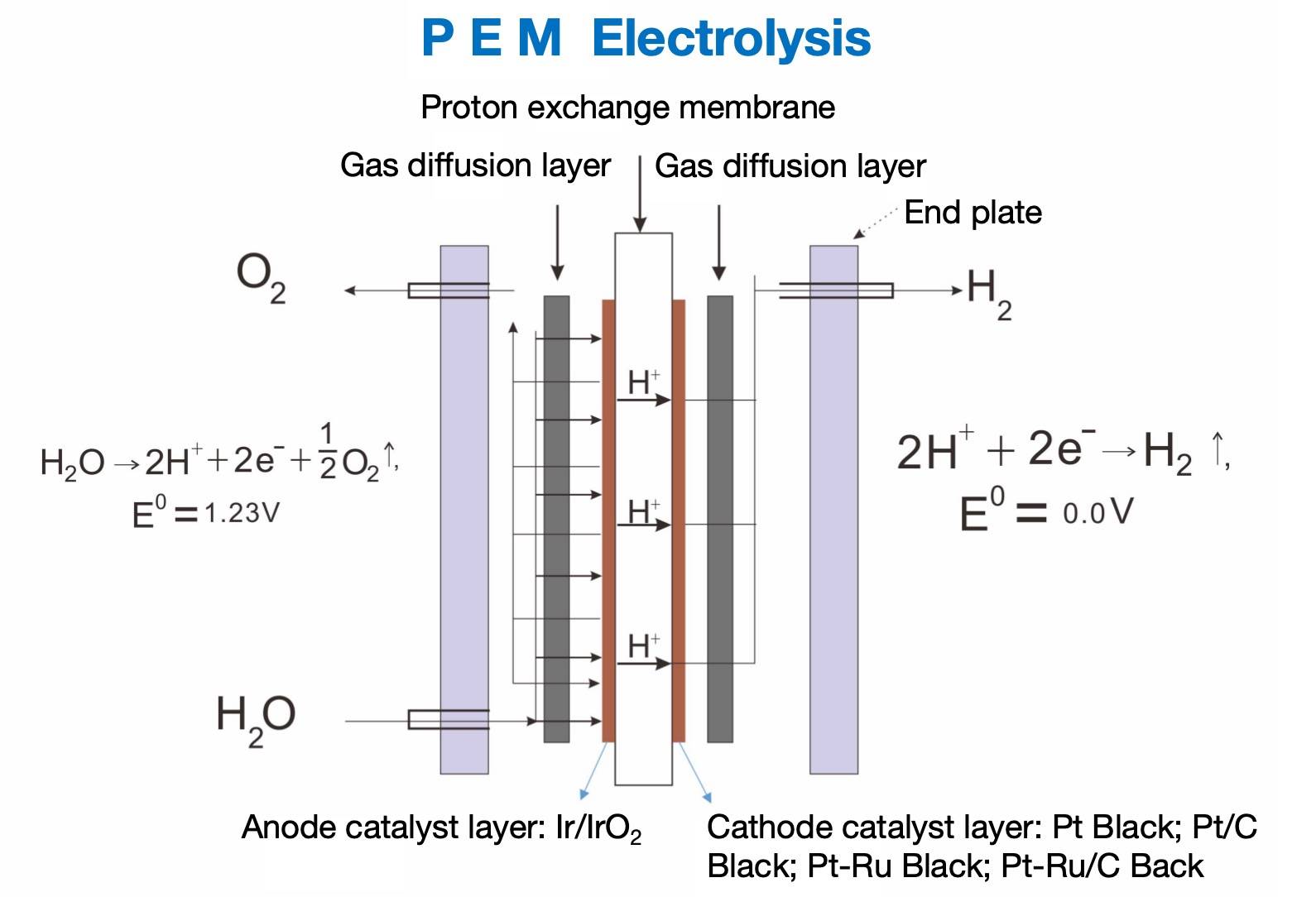
The anode catalyst for hydrogen production by PEM electrolysis is mainly Ir/IrO2, and the cathode electrocatalyst mainly uses Pt metal. At present, the cathode catalyst widely used usually refers to the platinum carbon black composite electrocatalyst, which can achieve high oxygen reduction activity and certain stability under acidic conditions. The biggest problem for precious metal platinum as a cathode catalyst at present is whether the catalytic activity can be maximized, and to achieve the desired effect we must attain a certain load of platinum. The activity of electrocatalysis should be improved while the loading capacity of platinum is reduced. This technology needs to make certain changes in macroscopic composition and microscopic morphology, and change the original structure to fundamentally solve the problem of effective utilization of catalysts. The electrocatalyst introduces ruthenium as a binary catalyst, which can effectively strip oxygen elements. The activity of platinum was enhanced, and the catalytic activity was significantly improved. The decomposition of water requires high electrical energy, which too much limits the catalysis of pure platinum, Ru can dissociate hydrogen and oxygen intermediates at a lower potential, greatly improving the oxidation capacity of the electrocatalyst. This is also the most widely used bifunctional mechanism.

